Operators in C are used to perform operations on data. There are different types of operators in C, each with its own purpose. Here is a summary of the different types of operators in C:
Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform basic arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Examples of arithmetic operators include:
+: Addition-: Subtraction*: Multiplication/: Division%: Modulus (remainder of a division)
Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables. Examples of assignment operators include:
=: Assignment+=: Addition assignment-=: Subtraction assignment
*=: Multiplication assignment
/=: Division assignment
%=: Modulus assignment
Relational Operators
Relational operators are used to compare values and determine their relationship. Examples of relational operators include:
==: Equal to!=: Not equal to<: Less than<=: Less than or equal to>: Greater than>=: Greater than or equal toLogical Operators
Logical operators are used to combine Boolean expressions and form more complex Boolean expressions. Examples of logical operators include:
&&: Logical AND||: Logical OR!: Logical NOT
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators are used to manipulate individual bits of data. Examples of bitwise operators include:
&: Bitwise AND|: Bitwise OR^: Bitwise XOR~: Bitwise NOT<<: Left shift>>: Right shift
Increment and Decrement Operators
Increment and decrement operators are used to increment (increase) or decrement (decrease) the value of a variable by 1. Examples of increment and decrement operators include:
++: Increment--: Decrement-768.png) image for geeksforgeeks
image for geeksforgeeks
what is an algorithm ? write an algorithm to check weather a number the given number is prime or not
An algorithm is a set of instructions that define a sequence of operations to be performed to solve a specific problem or accomplish a specific task. It is a step-by-step procedure that is designed to be executed by a computer or by a human.
Write an algorithm to find the given number is prime number or not?
Step 1 : start
Step 2 : Read the value in N
Step 3 : set f=0
Step 4 : for i=2 to N-1
step 5 : if N mod i =0 then set f=1
step 6 :if f=1 then print “ number is not a prime number”
else print “ number is a prime number “
step 7 : stop
what is Flow chart?
Flowchart is a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm. Flowchart is very helpful in writing program and
explaining program to others. Symbols Used In Flowchart
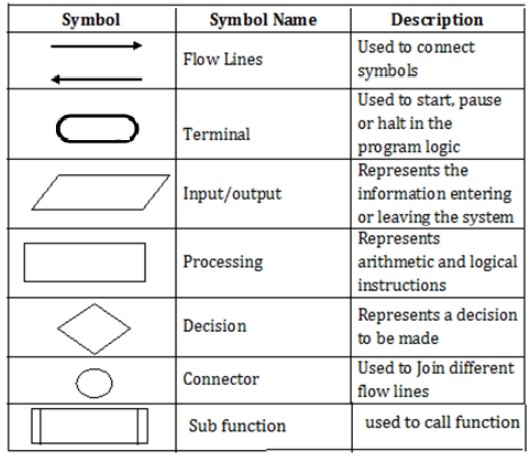 what are the different symbols used used in flow
what are the different symbols used used in flow
chart and give an example
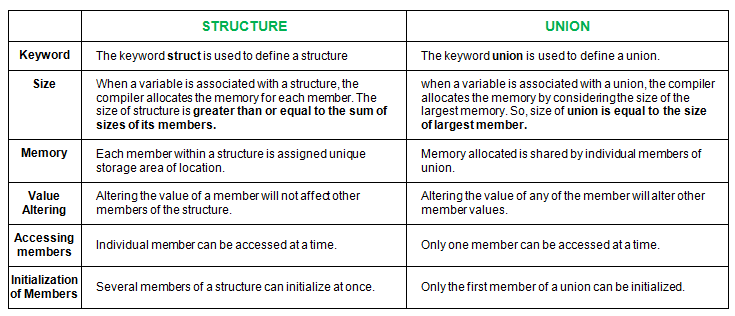
Explain in detail about the structure of c program with a sample program
The structure of a program is defined by its control flow , as structure are built up of blocks of codes.
These block have single entre and single exit ion the control flow.
* Documentation section
* The Link section
* The definition section
* Global Declaration section
* Every C program must have one main ( ) function section. This section contains two parts
declaration part and executable part
* The sub program section
DEFINITION OF ARRAYS
The array is a fixed-size sequenced collection of elements of same data type.
The array is a collection of homogeneous elements of same data type.
Array groups the data items of similar types sharing the common name.
Arrays are called as subscripted variables because; it is accessed using
TYPES OF ARRAYS
I. One dimensional arrays/Single-Subscripted Variable
II. Two dimensional arrays/Double-Subscripted Variable
III. Multidimensional arrays
I. One-Dimensional Arrays: A list of items can be given one variable name using only one subscript
and such a variable is called a single subscripted variable or one dimensional array.
Ex: int marks[4]
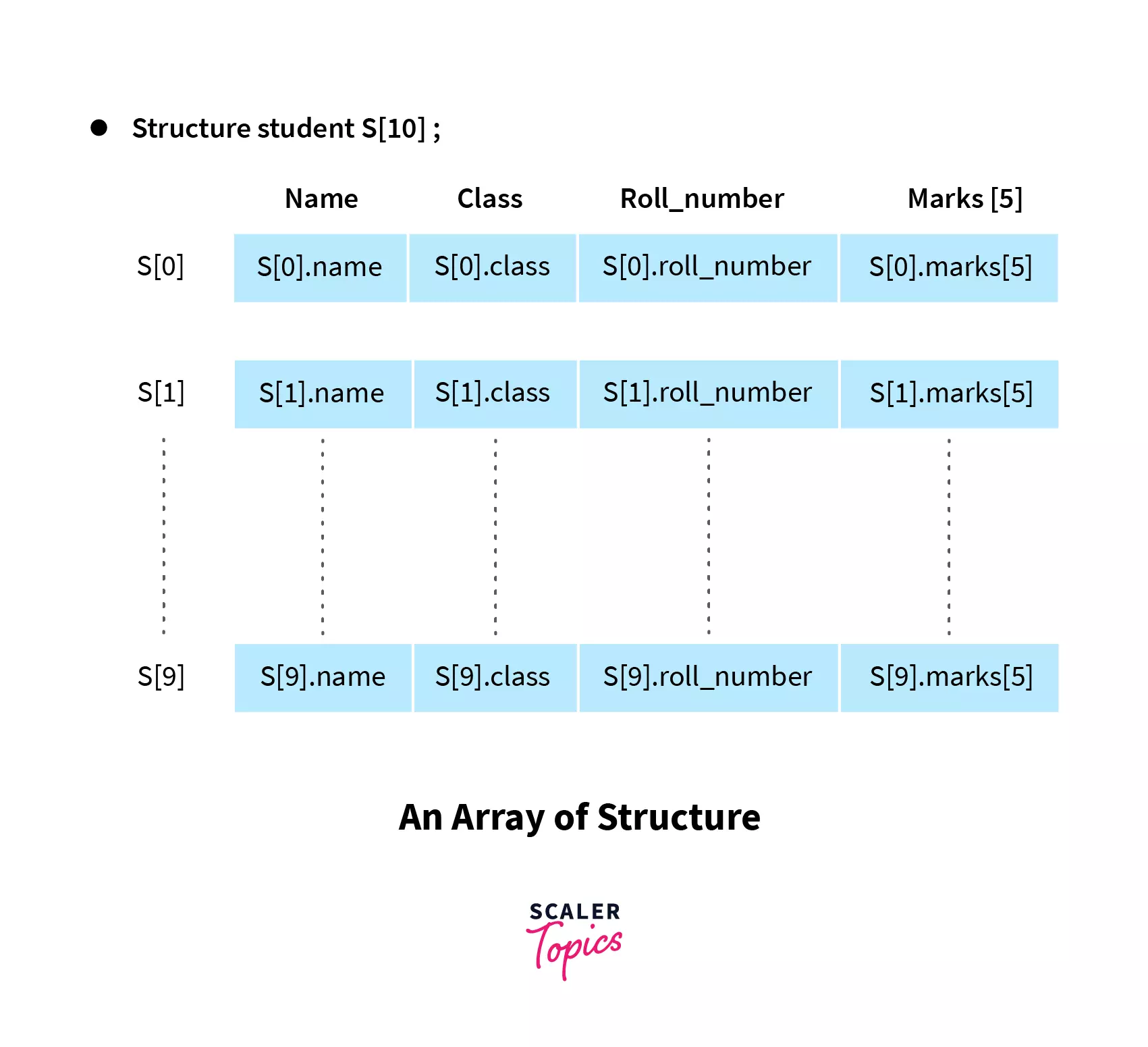
Array of Structures
-768.png)

Comments